 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Compare Bear Put Spread and Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) options trading strategies. Find similarities and differences between Bear Put Spread and Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) strategies. Find the best options trading strategy for your trading needs.
| Bear Put Spread | Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
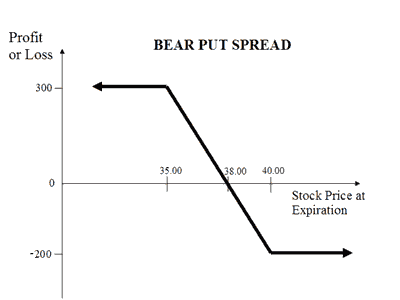
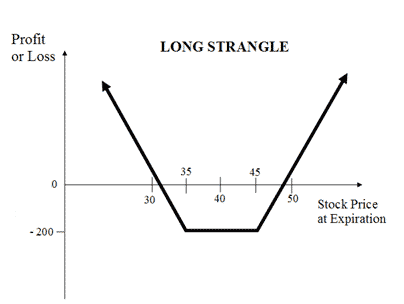
| About Strategy | The Bear Put strategy involves selling a Put Option while simultaneously buying a Put option. Contrary to Bear Call Spread, here you pay the higher premium and receive the lower premium. So there is a net debit in premium. Your risk is capped at the difference in premiums while your profit will be limited to the difference in strike prices of Put Option minus net premiums. This strategy is used when the trader believes that the price of underlying asset will go down moderately. This strategy is also known as the bear put debit spread as a net debit is taken upon entering the trade. This strategy has a limited risk as well as limited rewards. How to use the bear put spread options strategy? The bear put spread strategy looks like... Read More | The Long Strangle (or Buy Strangle or Option Strangle) is a neutral strategy wherein Slightly OTM Put Options and Slightly OTM Call are bought simultaneously with same underlying asset and expiry date. This strategy can be used when the trader expects that the underlying stock will experience significant volatility in the near term. It is a limited risk and unlimited reward strategy. The maximum loss is the net premium paid while maximum profit is achieved when the underlying moves either significantly upwards or downwards at expiration. The usual Long Strangle Strategy looks like as below for NIFTY current index value at 10400 (NIFTY Spot Price): Options Strangle Orders OrdersNIFTY Strike Price Buy 1 Slightly OTM PutN... Read More |
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| Strategy Level | Advance | Beginners |
| Options Type | Put | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 | 2 |
| Risk Profile | Limited | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium | two break-even points |
| Bear Put Spread | Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| When to use? | The bear call spread options strategy is used when you are bearish in market view. The strategy minimizes your risk in the event of prime movements going against your expectations. |
A Long Strangle is meant for special scenarios where you foresee a lot of volatility in the market due to election results, budget, policy change, annual result announcements etc. |
| Market View | Bearish When you are expecting the price of the underlying to moderately drop. |
Neutral When you are unsure of the direction of the underlying but expecting high volatility in it. |
| Action |
|
Suppose Nifty is currently at 10400 and you expect the price to move sharply but are unsure about the direction. In such a scenario, you can execute long strangle strategy by buying Nifty at 10600 and at 10800. The net premium paid will be your maximum loss while the profit will depend on how high or low the index moves. |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium The breakeven point is achieved when the price of the underlying is equal to strike price of long Put minus net premium. |
two break-even points A Options Strangle strategy has two break-even points. Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium |
| Bear Put Spread | Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| Risks | Limited The maximum loss is limited to net premium paid. It occurs when the price of the underlying is less than strike price of long Put.. Max Loss = Net Premium Paid. |
Limited Max Loss = Net Premium Paid The maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid in the long strangle strategy. It occurs when the price of the underlying is trading between the strike price of Options. |
| Rewards | Limited The maximum profit is achieved when the strike price of short Put is greater than the price of the underlying.. Max Profit = Strike Price of Long Put - Strike Price of Short Put - Net Premium Paid. |
Unlimited Maximum profit is achieved when the underlying moves significantly up and down at expiration. Profit = Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid Or Profit = Strike Price of Long Put - Price of Underlying - Net Premium Paid |
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Underlying goes down and both options exercised |
One Option exercised |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Underlying goes up and both options not exercised |
Both Option not exercised |
| Bear Put Spread | Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Risk is limited. It reduces the cost of investment. |
|
| Disadvantage | The profit is limited. |
The strategy requires significant price movements in the underlying to gain profits. |
| Simillar Strategies | Bear Call Spread, Bull Call Spread | Long Straddle, Short Strangle |

Add a public comment...

FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|