 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Published on Thursday, April 19, 2018 | Modified on Wednesday, June 5, 2019
| Strategy Level | Beginners |
| Instruments Traded | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 |
| Market View | Neutral |
| Risk Profile | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | 2 break-even points |
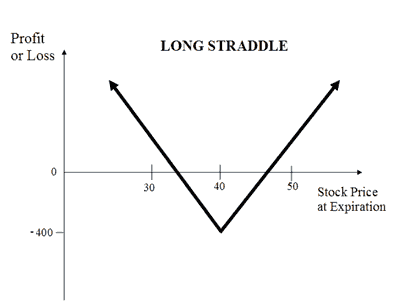
The Long Straddle (or Buy Straddle) is a neutral strategy. This strategy involves simultaneously buying a call and a put option of the same underlying asset, same strike price and same expire date.
A Long Straddle strategy is used in case of highly volatile market scenarios wherein you expect a big movement in the price of the underlying but are not sure of the direction. Such scenarios arise when company declare results, budget, war-like situation etc.
This is an unlimited profit and limited risk strategy. The profit earns in this strategy is unlimited. Higher volatility results in higher profits. The maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid. The max loss occurs when underlying asset price on expire remains at the strike price.
The usual Long Straddle Strategy looks like as below for NIFTY current index value at 10400 (NIFTY Spot Price):
| Orders | NIFTY Strike Price |
|---|---|
| But 1 Put Option | NIFTY18APR10400PE |
| Buy 1 Call Option | NIFTY18APR10400CE |
Suppose Nifty is currently at 10400 and due to some upcoming events you expect the price to move sharply but are unsure about the direction. In such a scenario, you can execute long strangle strategy by buying Nifty Put at 10400 and buying Nifty Call at 10400. The net premium paid will be your maximum loss while the profit will depend on how high or low the index moves.
The strategy is perfect to use when there is market volatility expected due to results, elections, budget, policy change, war etc.
Let's take a simple example of a stock trading at Rs 40 (spot price) in June. The option contracts for this stock are available at the premium of:
Lot size: 100 shares in 1 lot
Net Debit: Rs 200 + Rs 200 = Rs 400
Now let's discuss the possible scenarios:
Scenario 1: Stock price remains unchanged at Rs 40
The total loss of Rs 400 is also the maximum loss in this strategy.
Scenario 2: Stock price goes above Rs 50
Scenario 3: Stock price goes down to Rs 30
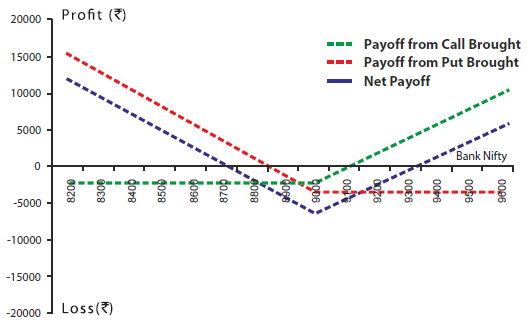
| Bank Nifty Spot Price | 8900 |
| Bank Nifty Lot Size | 25 |
| Strike Price(Rs ) | Premium(Rs ) | Total Premium Paid(Rs ) (Premium * lot size 25) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buy 1 Call | 9000 | 100 | 2500 |
| Buy 1 Put | 9000 | 200 | 5000 |
| Net Premium (200+100) | 300 | 7500 | |
| Upper Breakeven(Rs ) | Strike price of Call + Net Premium (9000 + 300) | 9300 |
| Lower Breakeven(Rs ) | Strike price of put - Net Premium (9000 - 300) | 8700 |
| Maximum Possible Loss (Rs ) | Net Premium Paid | 7500 |
| Maximum Possible Profit (Rs ) | Unlimited |
| On Expiry Bank NIFTY closes at | Net Payoff from 1 Call bought (Rs ) @9000 | Net Payoff from 1 Put Bought (Rs ) @9000 | Net Payoff (Rs ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8300 | -2500 | 12500 | 10000 |
| 8500 | -2500 | 7500 | 5000 |
| 8700 | -2500 | 2500 | 0 |
| 9000 | -2500 | -5000 | -7500 |
| 9300 | 5000 | -5000 | 0 |
| 9600 | 12500 | -5000 | 7500 |
| 10000 | 22500 | -5000 | 17500 |
When you are not sure on the direction the underlying would move but are expecting the rise in its volatility.
2 break-even points
A straddle has two break-even points.
Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium
Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium
The maximum loss for long straddle strategy is limited to the net premium paid. It happens the price of underlying is equal to strike price of options.
Maximum Loss = Net Premium Paid
There is unlimited profit opportunity in this strategy irrespective of the direction of the underlying. Profit occurs when the price of the underlying is greater than strike price of long Put or lesser than strike price of long Call.
Max profit is achieved when at one option is exercised.
When both options are not exercised. This happens when underlying asset price on expire remains at the strike price.
Earns you unlimited profit in a volatile market while minimizing the loss.
The price change has to be bigger to make good profits.

Add a public comment...

FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|