 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Published on Thursday, April 19, 2018 | Modified on Wednesday, June 5, 2019
| Strategy Level | Advance |
| Instruments Traded | Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 |
| Market View | Bearish |
| Risk Profile | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium |
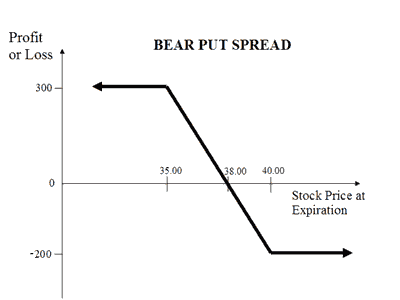
The Bear Put strategy involves selling a Put Option while simultaneously buying a Put option. Contrary to Bear Call Spread, here you pay the higher premium and receive the lower premium. So there is a net debit in premium. Your risk is capped at the difference in premiums while your profit will be limited to the difference in strike prices of Put Option minus net premiums.
This strategy is used when the trader believes that the price of underlying asset will go down moderately. This strategy is also known as the bear put debit spread as a net debit is taken upon entering the trade.
This strategy has a limited risk as well as limited rewards.
The bear put spread strategy looks like as below for NIFTY which are currently traded at Rs 10400 (NIFTY Spot Price):
| Orders | NIFTY Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Buy 1 ITM Put | NIFTY18APR10600PE |
| Sell 1 OTM Put | NIFTY18APR10200PE |
Suppose NIFTY shares are trading at 10400. If we are expecting the price of NIFTY to go down in near future, we buy 1 ITM NIFTY Put and sell 1 OTM NIFTY put to implement this strategy.
If NIFTY rises, your loss will be the net difference in premiums. If it falls, your profit will be the difference between two strike prices minus the net premium paid.
The bear call spread options strategy is used when you are bearish in market view. The strategy minimizes your risk in the event of prime movements going against your expectations.
Let's take a simple example of a stock trading at Rs 38 (spot price) in June. The option contracts for this stock are available at the premium of:
Lot size: 100 shares in 1 lot
Net debit: Rs 300 - Rs 100 = Rs 200
Now let's discuss the possible scenarios:
Scenario 1: Stock price remains unchanged at Rs 38
In this scenario no profit or loss is made.
Scenario 2: Stock price goes up to Rs 42
In this scenario, we lost total Rs 200 which is also the maximum loss in this strategy.
Scenario 3: Stock price goes down to Rs 34
Same as scenario 1:
This Rs 300 is also the maximum profit earned in this strategy.
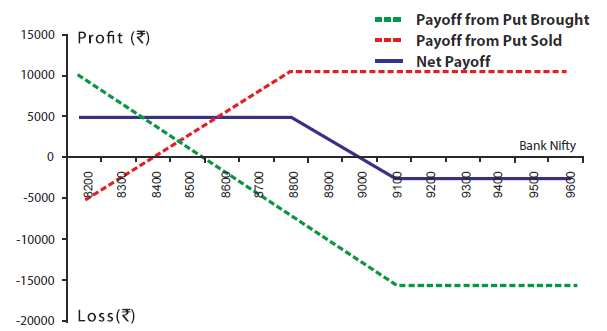
| Bank Nifty Spot Price | 8900 |
| Bank Nifty Lot Size | 25 |
| Strike Price(Rs ) | Premium(Rs ) | Total Premium Paid(Rs ) (Premium * lot size 25) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buy 1 ITM Put | 9100 | 500 | 12500 |
| Sell 1 OTM Put | 8800 | 400 | 10000 |
| Net Premium (500-400) | 100 | 2500 | |
| Breakeven(Rs ) | Strike price of the Long Put - Net Premium (9100 - 100) | 9000 |
| Maximum Possible Loss (Rs ) | Net Premium Received * Lot Size (100)*25 | 2500 |
| Maximum Possible Loss (Rs ) | (Strike Price of Long Put - Strike Price of Short Put - Net Premium Paid) * Lot Size (9100-8800-100)*25 | 5000 |
| On Expiry Bank NIFTY closes at | Net Payoff from 1 ITM Put Brought (Rs ) @9100 | Net Payoff from 1 OTM Put Sold (Rs ) @8800 | Net Payoff (Rs ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8600 | 0 | 5000 | 5000 |
| 8800 | -5000 | 10000 | 5000 |
| 9000 | -10000 | 10000 | 0 |
| 9200 | -12500 | 10000 | -2500 |
| 9400 | -12500 | 10000 | -2500 |
When you are expecting the price of the underlying to moderately drop.
Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium
The breakeven point is achieved when the price of the underlying is equal to strike price of long Put minus net premium.
The maximum loss is limited to net premium paid. It occurs when the price of the underlying is less than strike price of long Put..
Max Loss = Net Premium Paid.
The maximum profit is achieved when the strike price of short Put is greater than the price of the underlying..
Max Profit = Strike Price of Long Put - Strike Price of Short Put - Net Premium Paid.
Underlying goes down and both options exercised
Underlying goes up and both options not exercised
Risk is limited. It reduces the cost of investment.
The profit is limited.


FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|