 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Published on Thursday, April 19, 2018 | Modified on Wednesday, June 5, 2019
| Strategy Level | Beginners |
| Instruments Traded | Call + Underlying |
| Number of Positions | 2 |
| Market View | Bearish |
| Risk Profile | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Underlying Price - Call Premium |
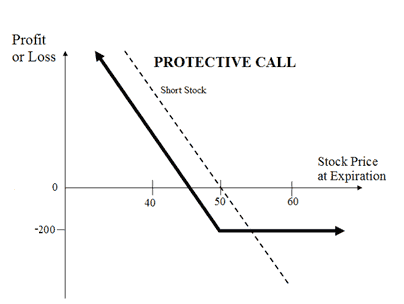
The Protective Call strategy is a hedging strategy. In this strategy, a trader shorts position in the underlying asset (sell shares or sell futures) and buys an ATM Call Option to cover against the rise in the price of the underlying.
This strategy is opposite of the Synthetic Call strategy. It is used when the trader is bearish on the underlying asset and would like to protect 'rise in the price' of the underlying asset.
The risk is limited in the strategy while the rewards are unlimited.
The usual Protective Call Strategy looks like as below for State Bank of India (SBI) Shares which are currently traded at Rs 275 (SBI Spot Price):
| Orders | SBI Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Sell Underlying Shares | Sell 100 SBI Shares at Rs 275 |
| Buy 1 ATM Call Option | SBI18APR275CE |
Suppose SBI shares are trading at Rs 275. You are of the view that the price will go down in near future and hence sell 100 shares. Now to protect yourself against a rise in the price and the resultant losses from it, you buy an ATM Call Option of SBI. If the price increases, your loss will be the difference between the strike price of call and strike price plus premium paid. If the prices fall, you will earn profits from the trade in underlying.
The Protective Call Strategy looks like as below for NIFTY which are currently traded at Rs 10400 (NIFTY Spot Price):
| Orders | NIFTY Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Sell NIFTY Futures | Sell 1 lot of NIFTY Future at Rs 10400 |
| Buy 1 ATM Call Option | NIFTY18APR10400CE |
Suppose NIFTY is trading at 10400. If we are expecting the price of NIFTY to go down in near future, we sell 1 lot of NIFTY future. Now to protect ourselves against the rise in the price, we buy an ATM Call Option of NIFTY. If NIFTY goes up, our loss will be the difference between the strike price of call and strike price plus premium paid. If the NIFTY goes down, we will earn profits from the futures as we shorted it.
The Protective Call option strategy is used when you are bearish in market view and want to short shares to benefit from it. The strategy minimizes your risk in the event of prime movements going against your expectations.
Let's take a simple example of a stock trading at Rs 50 (spot price) in June. The option contracts for this stock are available at the premium of:
Lot size: 100 shares in 1 lot
Now let's discuss the possible scenarios:
Scenario 1: Stock price remains unchanged at Rs 50
The total loss of Rs 200 is also the maximum loss in this strategy. This is the amount you paid a premium at the time you enter in the trade.
Scenario 2: Stock price goes to Rs 70
In this scenario, Rs 2000 is the loss made from shares shorted. We earned Rs 2000 from the Call options position which nullifies the trade. The net loss made in this transaction is Rs 200 premium paid to take the Call Options position. This is also the maximum loss in this strategy.
Scenario 3: Stock price goes down to Rs 30
In this scenario, Rs 2000 is the profit earn from shares shorted. We lost the premium paid for call position as it expired worthless. The net profit earned is Rs 1800.
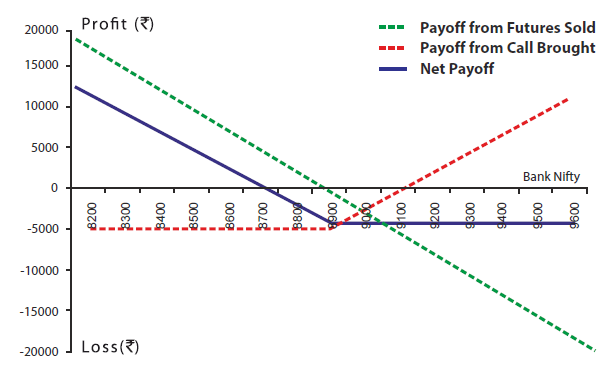
| Bank Nifty Spot Price | 8900 |
| Bank Nifty Lot Size | 25 |
| Strike Price(Rs ) | Premium(Rs ) | Total Premium Paid(Rs ) (Premium * lot size 25) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sell 1 Future Lot | 8900 | - | - |
| Buy 1 ATM Call Option | 8900 | 200 | 5000 |
| Net Premium | 200 | 5000 | |
| Breakeven(Rs ) | Future Price - Call Premium (8900 - 200) | 8700 |
| Maximum Possible Loss (Rs ) | Net Call Premium Paid | 5000 |
| Maximum Possible Profit (Rs ) | Unlimited |
| On Expiry Bank NIFTY closes at | Payoff on Future Sold (Rs ) @8900 | Payoff from 1 Call bought (Rs ) @8900 | Net Payoff (Rs ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8300 | 15000 (8900-8300)*25 | -5000 | 10000 |
| 8500 | 10000 (8900-8500)*25 | -5000 | 5000 |
| 8700 | 5000 (8900-8700)*25 | -5000 | 0 |
| 8900 | 0 (8900-8900)*25 | -5000 | -5000 |
| 9100 | -5000 (8900-9100)*25 | 0 (((9100-8900)*25)-5000) | -5000 |
When you are bearish on the underlying but want to protect the upside.
Underlying Price - Call Premium
When the price of the underlying is equal to the total of the sale price of the underlying and premium paid.
The maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for buying the Call option. It occurs when the price of the underlying is less than the strike price of Call Option.
Maximum Loss = Call Strike Price - Sale Price of Underlying + Premium Paid
The maximum profit is unlimited in this strategy. The profit is dependent on the sale price of the underlying.
Profit = Sale Price of Underlying - Price of Underlying - Premium Paid
Underlying goes down and Option not exercised
Underlying goes down and Option exercised
Minimizes the risk when entering into a short position while keeping the profit potential limited.
Premium paid for Call Option may eat into your profits.

Add a public comment...

FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|