 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
Zerodha (Trading & Demat Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Compare Short Call (Naked Call) and Covered Strangle options trading strategies. Find similarities and differences between Short Call (Naked Call) and Covered Strangle strategies. Find the best options trading strategy for your trading needs.
| Short Call (Naked Call) | Covered Strangle | |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
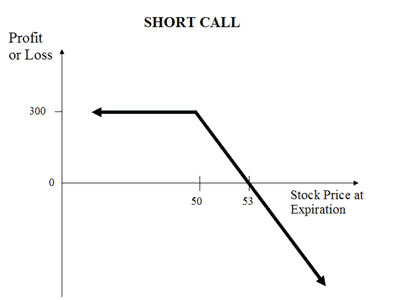
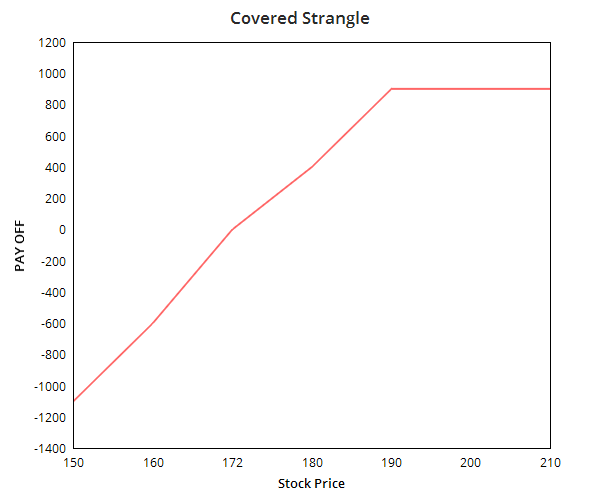
| About Strategy | Short Call (or Naked Call) strategy involves the selling of the Call Options (or writing call option). In this strategy, a trader is Very Bearish in his market view and expects the price of the underlying asset to go down in near future. This strategy is highly risky with potential for unlimited losses and is generally preferred by experienced traders. The strategy involves taking a single position of selling a Call Option of any type i.e. ITM or OTM. These naked calls are also known as Out-Of-The-Money Naked Call and In-The-Money Naked Call based on the type you choose. This strategy has limited rewards (max profit is premium received) and unlimited loss potential. When the trader goes short on call, the trader sells a call option and e... Read More | The covered strangle option strategy is a bullish strategy. The strategy is created by owning or buying a stock and selling an OTM Call and OTM Put. It is called covered strangle because the upside risk of the strangle is covered or minimized. The strategy is perfect to use when you are prepared to sell the holding or bought shares at a higher price if the market moves up but would also is ready to buy more shares if the market moves downwards. The profit and in this strategy is unlimited while the risk is only on the downside. |
| Market View | Bearish | Bullish |
| Strategy Level | Advance | Advance |
| Options Type | Call | Call + Put + Underlying |
| Number of Positions | 1 | 3 |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Short Call + Premium Received | two break-even points |
| Short Call (Naked Call) | Covered Strangle | |
|---|---|---|
| When to use? | It is an aggressive strategy and involves huge risks. It should be used only in case where trader is certain about the bearish market view on the underlying. |
A covered strangle strategy can be used when you are bullish on the market but also want to cover any downside risk. You are prepared to sell the shares on profit but are also willing to buy more shares in case the prices fall. |
| Market View | Bearish When you are expecting the price of the underlying or its volatility to only moderately increase. |
Bullish The Strategy is perfect to apply when you're bullish on the market and expecting less volatility in the market. |
| Action |
|
Buy 100 shares + Sell OTM Call +Sell OTM Put The covered strangle options strategy can be executed by buying 100 shares of a stock while simultaneously selling an OTM Put and Call of the same the stock and similar expiration date. |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Short Call + Premium Received Break even is achieved when the price of the underlying is equal to total of strike price and premium received. |
two break-even points There are 2 break-even points in the covered strangle strategy. One is the Upper break even point which is the sum of strike price of the Call option and premium received while the other is the lower break-even point which is the difference strike price of short Put and premium received. |
| Short Call (Naked Call) | Covered Strangle | |
|---|---|---|
| Risks | Unlimited There risk is unlimited and depend on how high the price of the underlying moves. |
Limited The risk on this strategy is only on the downside when the price moves below the strike price of the Put option. |
| Rewards | Limited The profit is limited to the premium received. |
Limited The maximum profit on this strategy happens when the stock price is above the call price on expiry. The profit is the total of the gain from buying/selling stocks and net premium received on selling options. |
| Maximum Profit Scenario | When underline asset goes down and option not exercised.
|
You will earn the maximum profit when the price of the stock is above the Call option strike price on expiry. You will be assigned on the Call option, would be able to sell holding shares on profit while retaining the premiums received while selling the options. |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | When underline asset goes up and option exercised.
|
The maximum loss would be when the stock price falls drastically and turns worthless. The premiums received while selling the options will compensate for some of the loss. |
| Short Call (Naked Call) | Covered Strangle | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | This strategy allows you to profit from falling prices in the underlying asset. |
|
| Disadvantage | There's unlimited risk on the upside as you are selling Option without holding the underlying. Rewards are limited to premium received only. |
|
| Simillar Strategies | Covered Put, Covered Calls, Bear Call Spread | Long Strangle, Short Strangle |

Add a public comment...

FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|